Difference between revisions of "Metadata specifications in context"
From filmstandards.org
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''From the [[TC 372 Workshop Compendium]]'' | ''From the [[TC 372 Workshop Compendium]]'' | ||
| − | Metadata, as the name implies, is data about data. In current usage of the term, the meaning of data is not restricted to digitally encoded information, but can be almost anything. | + | Metadata, as the name implies, is '''data about data'''. In current usage of the term, the meaning of data is not restricted to digitally encoded information, but can be almost '''anything'''. |
{| style="float: right; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: .46em 0 0 .2em;" | {| style="float: right; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: .46em 0 0 .2em;" | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| valign="top" width="405px" | | | valign="top" width="405px" | | ||
| − | The concept of metadata became popular about 15 years ago when it was realised that the emerging World Wide Web with all of its digital objects would need some equivalent to catalogue records. | + | The concept of metadata became popular about 15 years ago when it was realised that the emerging World Wide Web with all of its digital objects would need some '''equivalent to catalogue records'''. |
The ensuing development took a different course, however, with free text search engines becoming the major catalogues to the Web. | The ensuing development took a different course, however, with free text search engines becoming the major catalogues to the Web. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| valign="top" width="405px" | | | valign="top" width="405px" | | ||
| − | Metadata has been produced for centuries. Usually referred to as catalogues, some collections of metadata have become huge and complex works long before the advent of computers. | + | Metadata has been produced for centuries. Usually referred to as '''catalogues''', some collections of metadata have become huge and '''complex works''' long before the advent of computers. |
Cataloguing rules had to reflect this complexity, leading to an ever increasing number of clauses and directives. | Cataloguing rules had to reflect this complexity, leading to an ever increasing number of clauses and directives. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
One card for each item in the collection. | One card for each item in the collection. | ||
| − | This legacy lives on, even in some of the most recent metadata specifications. | + | This '''legacy lives on''', even in some of the most recent metadata specifications. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| valign="top" width="405px" | | | valign="top" width="405px" | | ||
| − | Plenty of metadata is produced by machines. | + | Plenty of metadata is '''produced by machines'''. |
| − | Embedding metadata in the medium ensures that it does not get lost (as long as the medium remains intact). | + | Embedding metadata '''in the medium''' ensures that it does not get lost (as long as the medium remains intact). |
<span style="color:olive; font-size:9pt"> | <span style="color:olive; font-size:9pt"> | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
Some would also subsume this under the concept of metadata. | Some would also subsume this under the concept of metadata. | ||
| − | This label is clearly ''about'' something. Its use and its content schema is even mandated by law. | + | This label is clearly ''about'' something. Its use and its '''content schema''' is even mandated by law. |
Assuming that fashion is not a primary business of film archives, we will henceforth narrow our focus on metadata about cultural heritage items in general, and audiovisual artefacts in particular. | Assuming that fashion is not a primary business of film archives, we will henceforth narrow our focus on metadata about cultural heritage items in general, and audiovisual artefacts in particular. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| valign="top" width="405px" | | | valign="top" width="405px" | | ||
| − | Defining metadata means defining structure. Basically, a metadata schema defines an artifical language, consisting of a vocabulary and a grammar. | + | Defining metadata means defining '''structure'''. Basically, a metadata schema defines an artifical language, consisting of a vocabulary and a grammar. |
| − | Marking up the artificial grammar elements in the example on the left will easily exhaust your stock of felt-tip pens. | + | Marking up the '''artificial grammar''' elements in the example on the left will easily exhaust your stock of felt-tip pens. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| valign="top" width="405px" | | | valign="top" width="405px" | | ||
| − | Librarians have devised a metadata standard in which elements are identified through a numbering scheme. Known as MARC (or variants thereof), this scheme | + | Librarians have devised a metadata standard in which '''elements''' are identified through a '''numbering scheme'''. Known as MARC (or variants thereof), this scheme |
has developed from modest beginnings in the 1960s into a family of complex specifications. Variants of MARC have been adopted by the majority of libraries worldwide. | has developed from modest beginnings in the 1960s into a family of complex specifications. Variants of MARC have been adopted by the majority of libraries worldwide. | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| valign="top" width="405px" | | | valign="top" width="405px" | | ||
| − | The image on the left shows metadata encoded in XML. This encoding uses human-readable names for its elements, and nesting (i.e. elements enclosed by elements) as a way of expressing structure. | + | The image on the left shows metadata encoded in XML. This encoding uses '''human-readable names''' for its elements, and nesting (i.e. elements enclosed by elements) as a way of expressing structure. |
XML has become the most widely used encoding for data and metadata exchange. | XML has become the most widely used encoding for data and metadata exchange. | ||
| − | It is largely neutral with respect to the semantics of data elements. Therefore, it can be used as an encoding for arbitrary data structures. | + | It is largely neutral with respect to the semantics of data elements. Therefore, it can be used as an encoding for '''arbitrary data structures'''. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
This is filmographic metadata represented in RDF/N3. | This is filmographic metadata represented in RDF/N3. | ||
| − | RDF (short for Resource Description Framework) is not actually an encoding, but a data model that can itself be encoded in different ways. Among others, it is the recommended representation for metadata using the Dublin Core element set, and for controlled vocabularies expressed using the SKOS model. | + | RDF (short for Resource Description Framework) is not actually an encoding, but a '''data model''' that can itself be encoded in different ways. Among others, it is the recommended representation for metadata using the Dublin Core element set, and for controlled vocabularies expressed using the SKOS model. |
Adoption of RDF has been slower than that of many other technologies, perhaps because of its more radical departure from established methods of representing data. | Adoption of RDF has been slower than that of many other technologies, perhaps because of its more radical departure from established methods of representing data. | ||
| − | One particular strength of RDF is that it facilitates integration of data from different models without the need for finding a ''least common denominator''. | + | One particular strength of RDF is that it facilitates '''integration of data''' from different models without the need for finding a ''least common denominator''. RDF has been chosen as the core for several activities collectively known as the ''Semantic Web''. |
| − | RDF has been chosen as the core for several activities collectively known as the ''Semantic Web''. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | {| height="20px" width="100%" | ||
| + | |- style="text-align:center; " | ||
| + | |<span style="color:#808080"> • [[TC 372 Workshop Compendium|Contents]] • Next: [[How EN 15744 and EN 15907 came into being]] • </span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
[[Category:TC 372 Compendium]] | [[Category:TC 372 Compendium]] | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 1 April 2011
From the TC 372 Workshop Compendium
Metadata, as the name implies, is data about data. In current usage of the term, the meaning of data is not restricted to digitally encoded information, but can be almost anything.
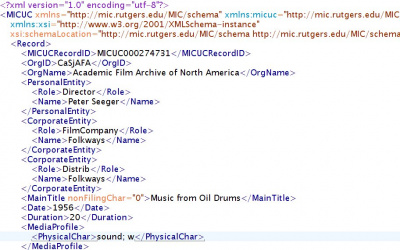 Part of a catalogue record from the Moving Image Collections portal, http://mic.imtc.gatech.edu/. Retrieved Oct, 2010 |
The image on the left shows metadata encoded in XML. This encoding uses human-readable names for its elements, and nesting (i.e. elements enclosed by elements) as a way of expressing structure. XML has become the most widely used encoding for data and metadata exchange. It is largely neutral with respect to the semantics of data elements. Therefore, it can be used as an encoding for arbitrary data structures. |
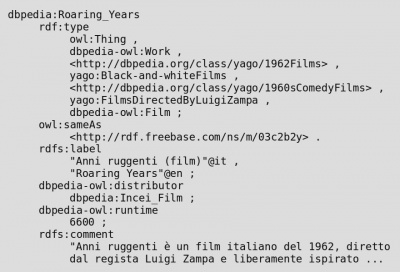 Selected statements from http://dbpedia.org/page/Roaring_Years. Retrieved March, 2011 |
This is filmographic metadata represented in RDF/N3. RDF (short for Resource Description Framework) is not actually an encoding, but a data model that can itself be encoded in different ways. Among others, it is the recommended representation for metadata using the Dublin Core element set, and for controlled vocabularies expressed using the SKOS model. Adoption of RDF has been slower than that of many other technologies, perhaps because of its more radical departure from established methods of representing data. One particular strength of RDF is that it facilitates integration of data from different models without the need for finding a least common denominator. RDF has been chosen as the core for several activities collectively known as the Semantic Web. |
| • Contents • Next: How EN 15744 and EN 15907 came into being • |






