From the TC 372 Workshop Compendium
The Agent entity
The Agent entity was deliberately left underspecified in EN 15907. This decision was made in order to facilitate interoperability among filmographic information systems with different data models.

|
Many bibliographic (and filmographic) database systems have used (and some are still using) a so-called flat file model. This is a model without many-to-many relationships (e.g. a person related to multiple works and a work related to multiple persons).
Data from flat-file systems typically has text fields filled with personal or corporate names, where the field name (or MARC tag number) represents the relationship with the work.
Data from such systems can be translated straightforwardly into an EN 15907 data structure by using the Agent Name and Activity elements of an Agent Relationship
|

|
The second method of handling an Agent Reference is to include descriptive data about the agent, encoded in a suitable format.
Evidently, this requires a relational data model in which data about agents (e.g. persons) is separated from film-related information, and joined via a many-to-many relationship.
Using this method, Agent descriptions can be transferred alongside with filmographic data. The drawback of this solution is that the person record may have to be transferred multiple times.
|
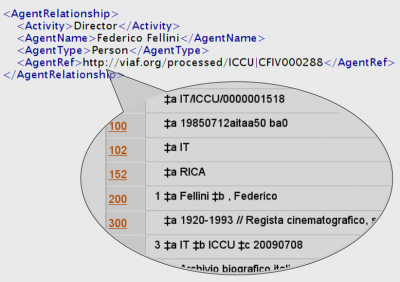
From: http://viaf.org/
|
The third method of handling an Agent Reference is to include a reference to a network resource with information describing the agent.
In this example, the reference points to a VIAF (virtual authority file) record obtained from the Istituto Centrale per il Catalogo Unico (ICCU).
EN 15907 permits any combination of agent references. Thus, if a database has references to external authority files for the more famous people and only names for the less famous, then both types can be used in a single data exchange.
|
The Event entity
The Event entity in EN 15907 is in fact a class of six event types that can occur in the lifecycle of a cinematographic work.


